Introduction
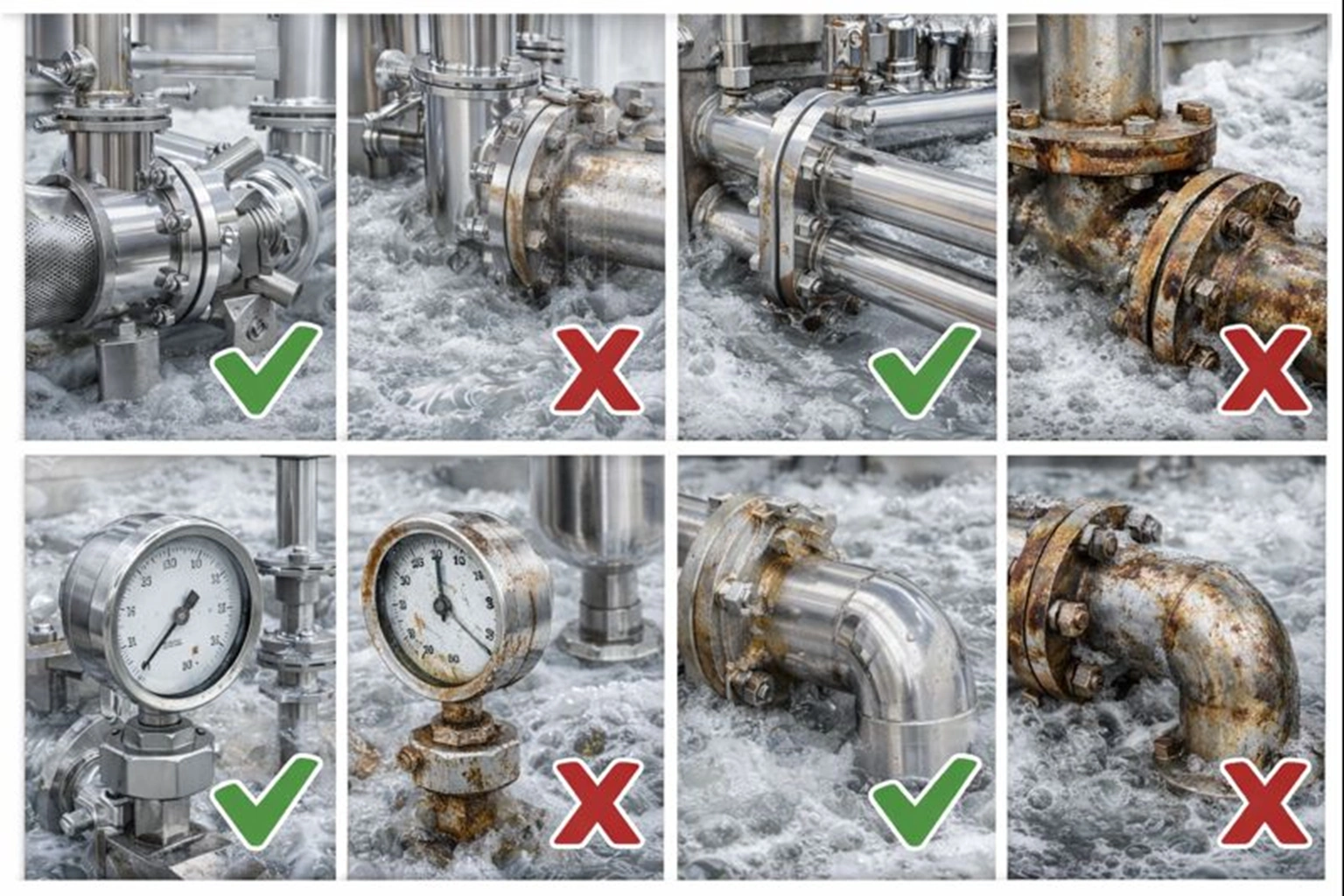
In spirulina farming, the choice of material for tanks, agitators, and processing equipment directly affects product safety, durability, and compliance with international food standards. Among various options, SS 316 (stainless steel grade 316) has become the global benchmark for spirulina cultivation and processing due to its superior corrosion resistance, hygiene, and compatibility with organic and HACCP-certified systems.
Using substandard materials such as plastic, aluminum, or mild steel can lead to contamination, nutrient degradation, and heavy metal leaching — all of which can compromise product quality and export compliance. In this article, we explore why SS 316 is the gold standard for every stage of spirulina production, from cultivation ponds to drying and packaging systems.
For compliance guidance, refer to How to Build a HACCP-Compliant Spirulina Facility.
What Is SS 316 Stainless Steel?
SS 316 is a molybdenum-alloyed austenitic stainless steel known for its enhanced resistance to corrosion, especially in chloride and saline environments. Its composition includes 16–18% chromium, 10–14% nickel, and 2–3% molybdenum, providing protection against rust, acids, and chemical exposure.
| Property | SS 304 | SS 316 | Significance for Spirulina Farming |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent | Essential for saline & alkaline ponds |
| Molybdenum Content | 0% | 2–3% | Prevents pitting in high pH environments |
| Chemical Compatibility | Limited | Broad | Suitable for nutrient-rich alkaline media |
| Cost | Lower | higher | Justified by longer lifespan and safety |
SS 316’s durability and chemical resistance make it ideal for continuous operation in the highly alkaline and nutrient-rich environment typical of spirulina cultivation systems.
Why SS 316 Is Critical for Spirulina Production
1. Corrosion Resistance in Alkaline Conditions
Spirulina grows best in pH 9–11, which is highly corrosive to most metals. SS 316’s molybdenum alloying ensures stability even in constant contact with alkaline media, preventing oxidation and leaching of metals into the culture.
2. Preventing Contamination
Unlike plastics or coated metals that degrade over time, SS 316 remains non-reactive and smooth. This prevents biofilm formation and cross-contamination, ensuring consistent microbial safety. For farms following USDA Organic or HACCP certification standards, this non-reactivity is mandatory.
3. Durability and Long-Term Value
Though initially costlier, SS 316 offers long-term savings by minimizing maintenance, replacement, and downtime. Equipment like agitators, harvesting drums, and drying trays made from SS 316 can last over a decade without corrosion.
4. Compliance with Food Safety Standards
International regulations such as FDA (U.S.), EFSA (Europe), and FSSAI (India) mandate food-contact equipment to be non-toxic and non-leaching. SS 316 complies with:
- HACCP and ISO 22000 standards for hygiene
- GMP guidelines for nutraceutical manufacturing
- EU food-contact material directives
5. Thermal and Mechanical Strength
Spirulina processing requires frequent temperature shifts during drying or sterilization. SS 316 maintains structural integrity under high temperatures and mechanical stress, ensuring safe operation in drying systems like Refractive Window Dryers (RWD) and vacuum dryers. (Spirulina Drying Methods: Comparison)
Applications of SS 316 in Spirulina Facilities
SS 316 is used across every stage of spirulina farming and processing due to its unmatched performance and regulatory compliance.
| Equipment | Material Requirement | Purpose |
| Raceway Pond Agitators | SS 316 Blades & Shafts | Ensures even mixing & prevents biofilm buildup |
| Harvesting Units | SS 316 Rotary Drum Filters | Hygienic separation of biomass from culture |
| Dewatering Systems | SS 316 Vacuum Chambers | Maintains pressure & prevents contamination |
| Drying Equipment | SS 316 Contact Surfaces | Retains nutrients & prevents oxidation |
| Packaging Line | SS 316 Filling & Sealing Systems | Ensures clean, contaminant-free packing |
| Laboratory Equipment | SS 316 Tanks & Benches | Meets GMP & HACCP standards |
Comparison: SS 316 vs. Other Materials
| Property | Mild Steel | Plastic (HDPE/PP) | SS 304 | SS 316 |
| Lifespan | 2–3 years | 5 years | 7–8 years | 10–15 years |
| Chemical Stability | Low | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
| Heat Resistance | Poor | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Hygienic Safety | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| Organic Certification Compliance | No | Conditional | Yes | Fully compliant |
As evident, SS 316 ensures the highest level of performance and compliance, making it indispensable for large-scale, export-oriented spirulina projects.
Economic Perspective
While SS 316 equipment may increase capital investment by 10–15% initially, it significantly reduces long-term operational costs. It eliminates frequent replacement of corroded parts, reduces maintenance time, and prevents costly contamination incidents that can cause full batch losses.
| Parameter | Plastic Equipment | SS 316 Equipment |
| Initial Cost | Low | Moderate |
| Annual Maintenance | High | Minimal |
| Risk of Contamination | High | Negligible |
| Life Span | 5 years | 15+ years |
| ROI (10-year period) | Low | High |
Long-term profitability in spirulina farming depends on reliability and compliance — both of which are assured with SS 316 infrastructure.
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
SS 316 aligns with sustainable production goals. It is 100% recyclable, has a long lifecycle, and supports closed-loop design principles. By reducing replacement frequency and waste, it contributes to the environmental sustainability of the overall production process. Learn more about sustainability practices in Is Spirulina Farming Sustainable?.
FAQs
Q1: Why not use SS 304 instead of SS 316?
SS 304 lacks molybdenum, making it more susceptible to corrosion in alkaline or saline conditions typical in spirulina ponds.
Q2: Can HDPE or plastic tanks be used for small-scale farms?
Yes, for pilot-scale or non-organic setups, HDPE tanks are acceptable but require strict maintenance and frequent replacement.
Q3: Does SS 316 affect the nutrient composition of spirulina?
No, it’s non-reactive and ensures that the product remains free from metallic contamination or oxidation.
Q4: Is SS 316 mandatory for export certification?
While not explicitly mandated, most HACCP, GMP, and organic certification audits require food-contact surfaces to be SS 316-grade or equivalent.
Q5: What is the expected lifespan of SS 316 equipment?
With proper cleaning and maintenance, SS 316 components can last over 15 years, offering excellent ROI for large-scale commercial farms.
Conclusion
In spirulina farming, where hygiene, safety, and consistency define success, SS 316 stainless steel remains the undisputed standard. Its superior corrosion resistance, compliance with global food regulations, and long lifespan make it essential for farms targeting international markets.
By investing in SS 316 equipment — from raceway agitators to dryers and packing systems — farmers can ensure contamination-free production, extend equipment life, and meet HACCP, USDA Organic, and EU food safety standards. Ultimately, SS 316 is not just a material choice; it’s a long-term investment in reliability, sustainability, and global compliance for the spirulina industry.