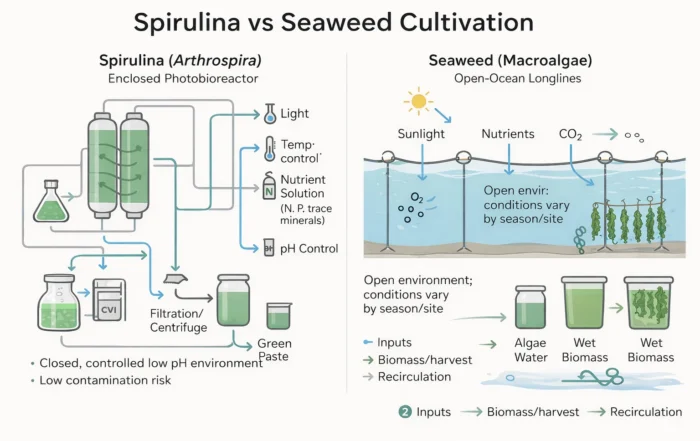
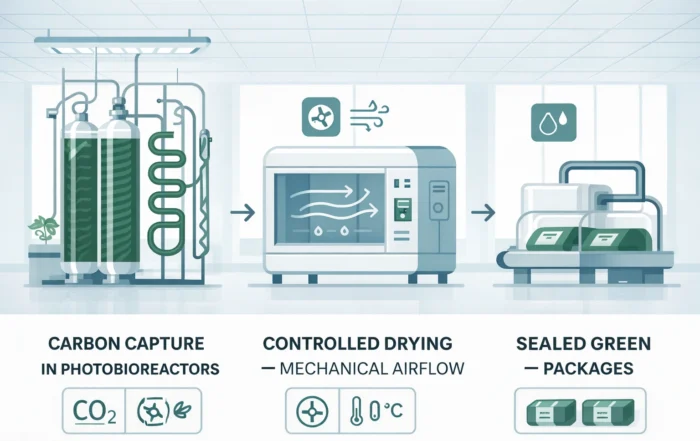
For most spirulina farms, compliance is treated as a downstream requirement – something to be addressed once production stabilises. The Nestling Agronomy project in Kovilpatti, Tamil Nadu, took a fundamentally different approach. Here, compliance was embedded into infrastructure design from the outset, resulting in what is now recognised as one of the world’s most energy-efficient spirulina production facilities.
This article examines how HACCP-aligned thinking, engineering discipline, and turnkey execution combined to create a facility where efficiency, hygiene, and scalability reinforce each other rather than compete.
Project Context: Engineering Precision Meets Nutraceutical Farming
Nestling Agronomy Pvt Ltd was founded by Mr. Chandrashekar, a pioneer in textile quality machinery from Coimbatore, along with his son. Coming from a background where precision, repeatability, and energy efficiency are non-negotiable, the transition into spirulina farming was approached as an engineering challenge rather than an agricultural experiment.
The project site in Kovilpatti was envisioned as a benchmark facility – one capable of producing high-quality spirulina with minimal environmental footprint while meeting global compliance expectations.
Why HACCP Was Treated as an Infrastructure Problem
Rather than layering HACCP documentation onto an existing farm layout, the Nestling Agronomy project treated HACCP as a design framework. This meant identifying critical control points early and shaping infrastructure around them.
Key priorities included:
- Controlled material flow from cultivation to drying
- Clear segregation of clean and non-clean zones
- Minimisation of manual handling
- Predictable, auditable process steps
This approach reduced dependence on behavioural controls and shifted compliance enforcement into physical design.
Greenbubble’s Role: From Concept to Turnkey Execution
Greenbubble’s involvement spanned consulting, machinery supply, and turnkey implementation. Rather than acting as a fragmented vendor, Greenbubble assumed responsibility for aligning equipment selection, layout planning, and execution with HACCP principles.
This integrated role ensured that compliance requirements were not compromised during cost optimisation or construction adjustments – a common failure point in large projects.
Designing for Energy Efficiency Without Compromising Hygiene
One of the defining achievements of the Nestling Agronomy facility is its exceptionally low electrical consumption per acre. Achieving this while maintaining hygienic integrity required careful system integration.
Greenbubble deployed high-efficiency harvesting equipment to reduce energy draw during biomass collection while maintaining controlled handling. Infrastructure layouts were optimised to minimise unnecessary movement and reprocessing.
Drying as a Critical Control Point
Drying is one of the most sensitive stages in HACCP-compliant spirulina production. At Nestling Agronomy, this stage was engineered for both energy efficiency and contamination control.
The facility uses the Nature Drive Window Dryer, a proprietary implementation of RWD drying systems, which allows low-temperature, high-efficiency moisture removal. This reduces thermal degradation while ensuring predictable, auditable drying outcomes.
By integrating drying tightly with upstream harvesting and downstream handling, the project eliminated common cross-contamination risks associated with intermediate storage.
Infrastructure-Level HACCP Controls
Instead of relying heavily on operator intervention, the Nestling Agronomy facility embeds HACCP controls into infrastructure:
- Defined physical pathways for material movement
- Equipment-driven process consistency
- Reduced touchpoints across stages
- Energy-efficient systems that maintain stable operating conditions
This design philosophy reduces variability, simplifies audits, and lowers long-term compliance overhead.
Execution Challenges and On-Ground Solutions
Implementing a highly engineered facility in a non-industrial rural setting presented challenges, including power stability, climate variability, and vendor coordination.
Greenbubble addressed these through:
- Turnkey project management to avoid responsibility gaps
- On-site supervision during critical installation phases
- Engineering redundancies where environmental variability was unavoidable
This execution discipline ensured that HACCP intent survived real-world constraints.
Outcomes: Efficiency as a Compliance Enabler
The Nestling Agronomy project demonstrates that compliance and efficiency are not opposing goals. By integrating HACCP into infrastructure design, the facility achieved:
- World-leading energy efficiency per acre
- Simplified compliance documentation and audits
- Reduced operational variability
- A scalable model for future expansion
Rather than adding cost, compliance became a driver of operational excellence.
What Other Spirulina Projects Can Learn
Key takeaways from the Nestling Agronomy project include:
- Treat compliance as a design input, not a paperwork exercise
- Engineer out risk wherever possible
- Energy efficiency strengthens, rather than weakens, hygiene control
- Turnkey accountability reduces long-term compliance gaps
These lessons are particularly relevant for farms targeting export or nutraceutical markets.
Greenbubble’s Approach to HACCP-Aligned Infrastructure
In projects like Nestling Agronomy, Greenbubble’s role extends beyond supplying machinery. By integrating consulting, equipment, and execution into a single responsibility framework, Greenbubble ensures that HACCP principles are physically embedded into farm infrastructure.
This approach allows spirulina producers to scale without accumulating hidden compliance risks.
FAQs
Q1. Is HACCP mandatory for spirulina farms?
HACCP is not always legally mandatory, but it is increasingly expected by nutraceutical buyers and export markets.
Q2. Does HACCP compliance increase capital costs?
Initial investment may increase, but lifecycle costs often decrease due to reduced rework, waste, and audit failures.
Q3. Can energy-efficient systems still meet hygiene standards?
Yes. When designed correctly, energy efficiency and hygiene reinforce each other rather than conflict.
Q4. Is turnkey execution important for compliance-heavy projects?
Yes. Fragmented responsibility often leads to gaps that undermine compliance.
Q5. Can this model be replicated at smaller scales?
The principles are scalable, though implementation details vary with capacity.
Conclusion: Compliance by Design, Not Addition
The Nestling Agronomy project illustrates that HACCP compliance does not have to be layered onto spirulina farming as an afterthought. When infrastructure is designed with compliance, efficiency, and scalability in mind from day one, farms achieve stronger operational control and long-term resilience. In this model, compliance is not a cost centre – it is a design advantage.